|

'Strobotron' lamps became popular during the 1930's as a light source intended for producing high energy light pulses of extremely short duration. See also CV310
In effect they function rather like a thyratron valve. The anode is a cup shaped electrode at the top end of the tube, usually consisting of iron or nickel with a coating of pure caesium over its surface for good electron emission. The cathode is similarly shaped and mounted directly above the glass stem press. This is separated from the so-called 'grid' electrode by a graphite cylinder with a small hole at its centre.
A DC voltage of about 220 to 380 V should be applied across the tube, typically from small capacitors of only about 1 to 10 5F. Then with a relatively low trigger voltage of only around 70 V or so at the grid, the neon gas filling will break down. The resulting discharge takes the form of an intensely bright narrow column running the length of the tube, and with the aid of a small specular parabolic reflector, a very bright beam of light can be projected that is clearly visible in daylight. Although the flash of light only lasts for about 10 milliseconds, the current is of the order of several hundred amperes, resulting in a very high intensity flash.
The lamps found widespread applications both in traditional stroboscopic type equipment, and in specialised units that were driven from the high tension ignition circuit in an automotive engine, producing synchronised pulses of light to assist in adjusting its timing. They were widely used until the 1960s when the Xenon flash tubes were introduced, offering higher intensity and the advantage of a white coloured flash. See LSD3.
The 631-P1 illustrated was a Sylvania Electric Products device. Basic operating details are: Anode Voltage: 220 - 380 VDC, Trigger Voltage: 70 VDC, Typical Anode Current: 100 mA. The base was UX4 and the grid was a graphite ring. Maximium flash rate: 200 Hz. Produced from about 1950.
The connections are: 1: Grid, 2: Anode, 3: inner Grid, 4: Cathode.
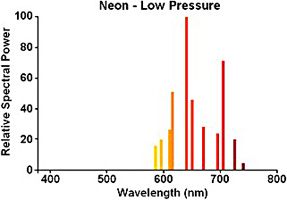
The gas used was neon at a pressure of 15 torr

|